
Healthcare systems, medical devices, and software often operate in isolation, resulting in siloed patient information, interoperability hurdles, and limited real-time insights. This data fragmentation hampers effective patient care coordination, decision-making, and operational efficiency. In some cases, healthcare providers need something from patients regularly but do not necessarily want a special trip by the healthcare providers to visit the patients every time. However, the current methods and systems do not allow healthcare providers to take care of these issues without having them to visit the patients every time.
This patented technology offers a transformative method and system for seamless task scheduling, execution, and monitoring, optimizing healthcare workflows. Employing predefined rules in certain environments, real-time notifications, and adaptive updates, it ensures efficient task management, empowering healthcare professionals for timely, patient-centric care without actually visiting the patients each time.
The patented technology can find applications in several areas such as:
- Telemedicine and remote monitoring
- Hospital at Home Care
- Healthcare task management
- Patient care coordination
- Patient engagement
- Medication management
Streamlined Protocol Documentation and Automation in Healthcare
The patented technology introduces a comprehensive computer-implemented system designed to revolutionize protocol documentation, automation, and compliance within the realm of safety-critical medical devices and patient care. This innovative ecosystem embodies a collaborative approach, addressing the intricate challenges faced by healthcare industries, life sciences, and medical devices. Its core function is to enable the streamlined management and execution of protocols and worklists across diverse medical devices, disciplines, and stakeholders, focusing on automation in healthcare.
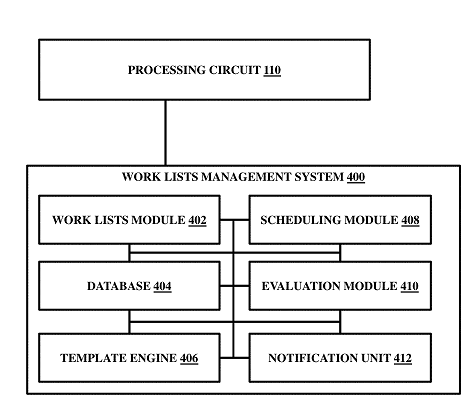
Figure 1
At its core, the system orchestrates a dynamic framework where protocols serve as shared baselines, guiding the execution of tasks across a multitude of safety-critical devices, each designed to collect and generate patient data. This facilitates synchronized and efficient patient care, eliminating variations and ensuring scalability, repeatability, and compliance. The system’s adaptability shines through its capacity to accommodate customized patient-centric variations while maintaining adherence to established protocols.
Patient-Centric Care: Automation with Personalization
In practice, the system offers far-reaching benefits, particularly in regulated industries where process-driven approaches are crucial for patient safety. The system excels in creating, coordinating, and automating complex care plans, bridging various organizational boundaries through its integration-friendly design. Notably, it enables patients to actively manage their health, engage in personalized care plans, and seamlessly communicate with healthcare professionals, all from the comfort of their homes.
A key innovation is the integration of WiFi-enabled devices within an interaction zone where the system is deployed, enhancing task management through real-time monitoring and event-triggered actions. Furthermore, the system empowers stakeholders from diverse disciplines, institutions, and organizations to collaboratively contribute to executable worklists, fostering efficient distributed workflows.
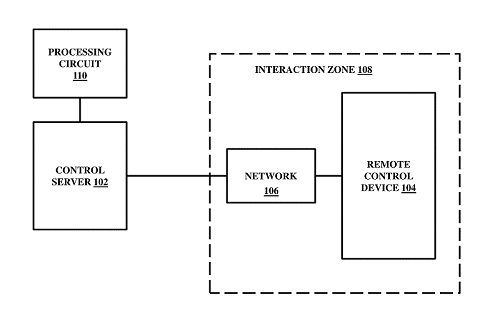 Figure 2
Figure 2
Through a carefully crafted blend of software and hardware elements, the invention brings forth a novel paradigm in medical care. It enables the automation of routine tasks, ensuring precision and timeliness, while offering the flexibility for modifications to suit unique patient needs. The resulting impact spans optimized clinical operations, reduced procedural overuse, enhanced medication administration, and a robust statistical framework for continuous improvement.
Ultimately, this inventive system provides a dynamic, adaptable, and interconnected platform that redefines medical protocol execution and patient care. By enabling the seamless collaboration of healthcare professionals, patients, and devices, it ushers in an era of streamlined, patient-centric, and compliance-driven medical practices.
Task Scheduling and Execution: A Closer Look at the Patent’s Innovation
In the patented technology, there’s a special computer (processing circuit and control server) that keeps track of time and events. It creates a timeline that shows when things should happen. This special computer also decides what needs to be done now and what’s coming up soon. It plans out a list of tasks that need to be completed. These tasks can include things like questionnaires, tests, process checks, guidelines, and more. They’re all things that can be changed and carried out at a specific time in the future. The computer system sets up rules that say when certain tasks should happen based on specific events. It knows when to start tasks because of these rules.
Different people can be part of this system, and the rules apply to them too. So, when the right event occurs, the system tells the people to start their tasks. There’s a device that can detect when the event happens. When it detects the event, it tells the computer system. The system checks who’s supposed to do the task. It does this by looking at an identification card that the person uses. This card is read by a special device that’s connected to the computer system.
Once the system knows who the task should do, it sends a message to their device. This message includes what needs to be done and how to do it. The message travels through a network of connected devices and includes instructions to start the task.
When the person gets instructions on their device, they know it’s time to start the task. They follow the instructions and do what needs to be done.
After they finish the task, they send a message back to the system. This message lets the system know that the task is done and gives information about how it went.
Based on how the task went and the information from the person’s message, the system might change the timeline. It decides if the task was successful and adjusts the schedule accordingly.
This adjusting of the schedule might mean changing when something was supposed to happen in the future. It’s like updating a calendar to reflect what’s really going on.
All these changes and adjustments are made by the system to make sure things run smoothly. It’s like having a helper that keeps everything organized and on track, especially when someone’s health is involved. A flow diagram of these actions is shown in FIG, 3 as follows.
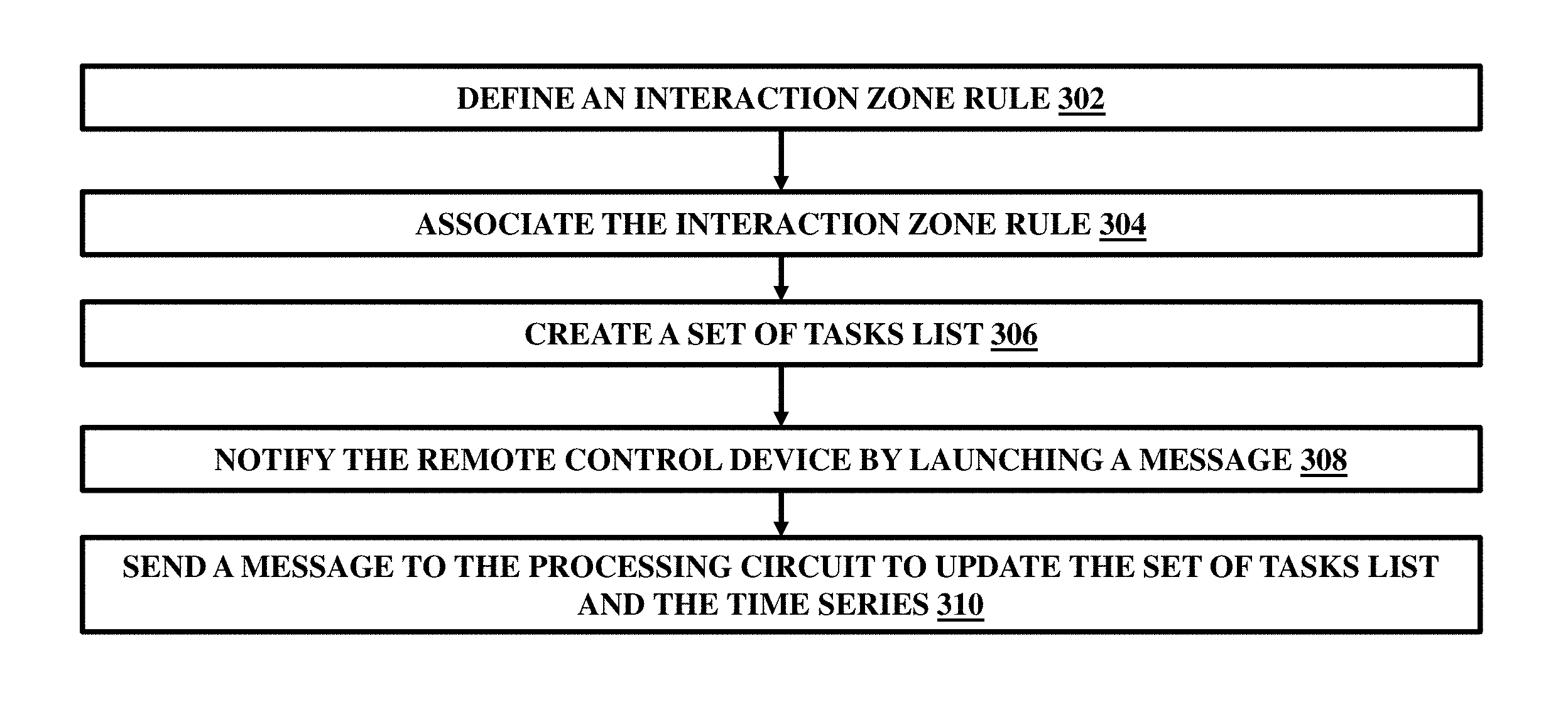 Figure 3
Figure 3
A user can use a special dashboard or interface like the one shown in Figures 4 and 5 below to connect with the system. This dashboard is designed to make it easy for the user to use the system that helps manage work lists. It’s like a control center where the user can choose different options and do things with your work lists. The dashboard has different sections that show things like the groups or organizations you’re a part of, the projects you’re working on, the people involved, and even ways for you to give feedback. It also displays details about the checklists or lists of tasks you have. It’s like a hub where you can see and manage all your work-related things.
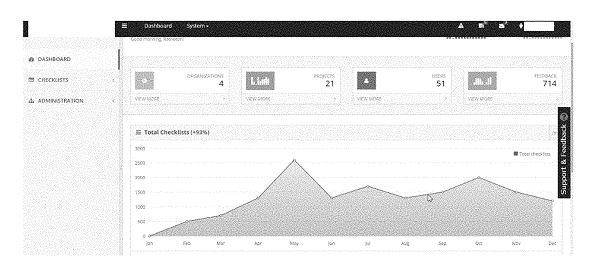 Figure 4
Figure 4
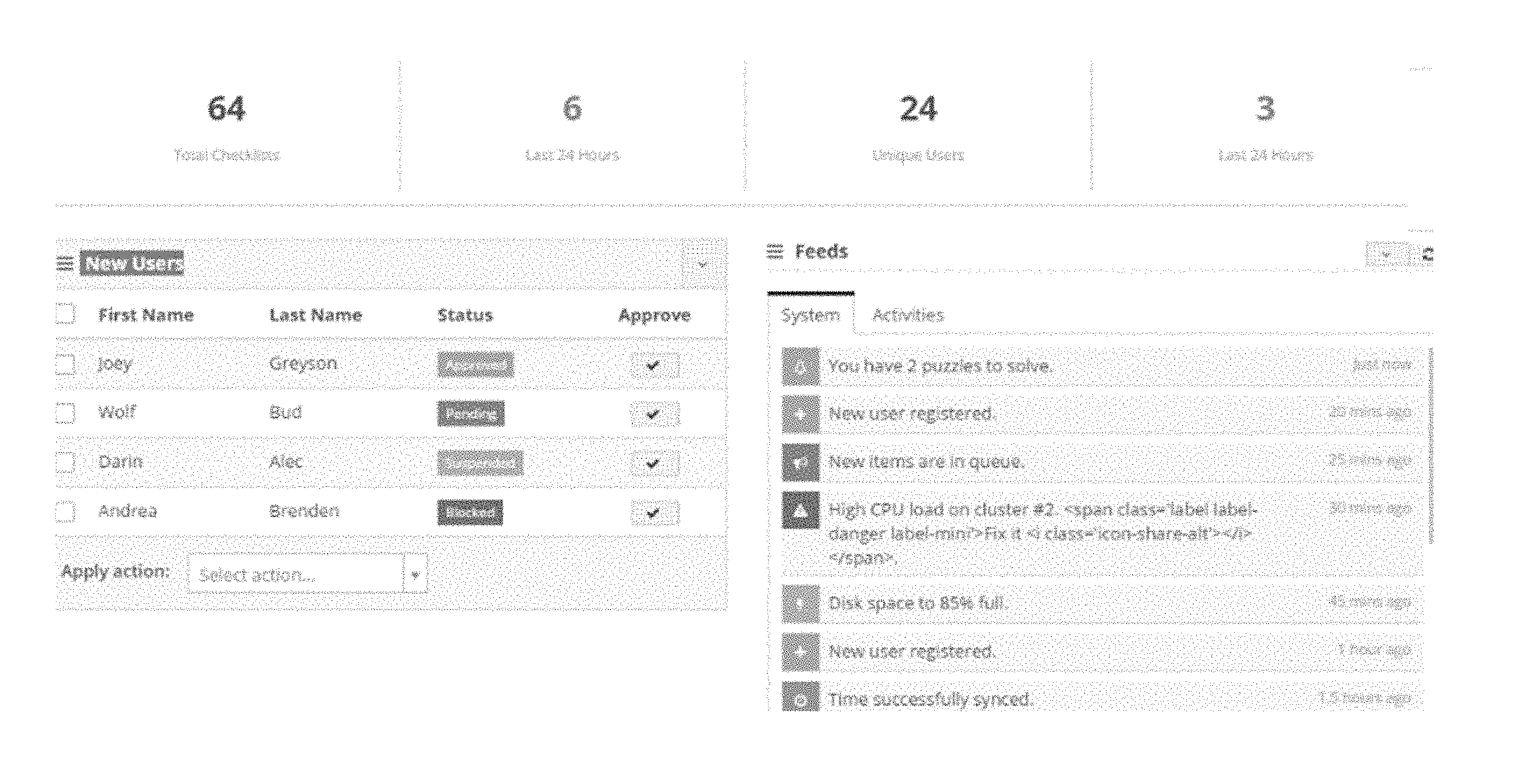 Figure 5
Figure 5
Figures. 6 and 7 show interfaces to manage the worklists, access different libraries, and automating tasks with scripts. In these user interfaces, there are tabs that work like buttons, and each tab helps you open different sections or “libraries” in this digital workspace. These libraries are like organized collections of things. There’s a library for projects, one for work lists (lists of tasks), another for tasks themselves, and even more like roles, forms, and scripts. It’s kind of like having separate drawers for different types of things, all neatly organized.
 Figure 6
Figure 6
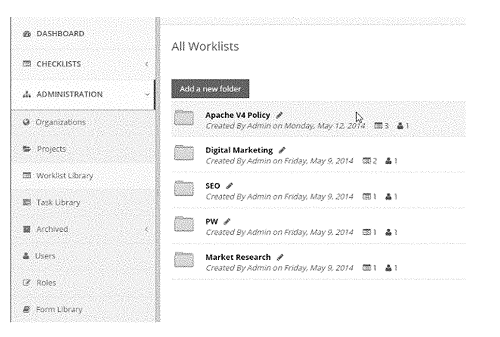 Figure 7
Figure 7
One of these libraries is for work lists. Each work list can have tasks related to it. You can make new work lists or change the ones you have. It’s like making a new to-do list or editing the old ones, but it’s all digital.
Another library is for tasks. It’s like a catalog of tasks you might need to do. Some of them are ready to use, like pre-made forms you can fill out. You can pick a task based on what it’s about, like software or networking, and add it to your work list. It’s almost like dragging and dropping things from one place to another.
There’s also a library for forms, like templates you can use. If you need a certain type of form, you can import it to your work list and fill in the details. And there’s another library for roles, which are like different job titles or positions. Each role has different permissions, like who can do what in the digital workspace.
Lastly, there’s a script library. Think of scripts like little bits of code that can do things automatically. So, after you finish a task, a script can make something happen, like sending a message to another part of the system.
The image below shows the different types of libraries available for functioning of the system.
 Figure 8
Figure 8
Efficient work management simplified through the patented technology in healthcare and other settings
The system helps industries like healthcare run their operations smoothly and in the right order. This system acts like a digital guide, making sure everything happens the way it should.
For industries that have rules to follow, like healthcare, this system is a game-changer. It ensures that tasks, procedures, and rules are followed step by step and on time. The system makes sure doctors and staff do everything they’re supposed to do, like taking care of patients or following guidelines.
But this system isn’t just for healthcare. It can be used in lots of places. It helps manage tasks and projects in a variety of scenarios. It can be used to create to-do lists for different things, like tests, questionnaires, and more. It’s even useful for complex things like coordinating care plans and procedures across different parts of a big organization.
This system is user-friendly. It’s like having a tool that can be adjusted to fit different needs. You can add comments, attach files, and even run special codes to make things happen automatically. And if you need a specific type of list, you can create it or import it from somewhere else.
Even patients with chronic conditions can benefit. They can manage their health using this system from home. It can remind them to take medicine, exercise, or even stick to a diet.
Industries like biotech and life sciences can use this system to keep track of things like drug research tasks and clinical trials. It ensures that important steps are taken and that rules are followed. Even social media managers can benefit. They can use the system to manage their tasks, like planning posts and campaigns.
