The healthcare sector is undergoing a rapid digital revolution, with electronic medical records becoming the backbone of patient care and administrative processes. According to recent studies, the global healthcare cybersecurity market is expected to reach $35.3 billion by 2028, reflecting the increasing recognition of the importance of securing sensitive patient information.
This huge market potential may be attributed to the following reasons.
Rising Threat Landscape
The healthcare industry has witnessed a surge in cyber threats, ranging from ransomware attacks to data breaches. Hackers are exploiting vulnerabilities in outdated systems, leveraging advanced tactics to compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of medical records.
Expanding Attack Vectors
With the proliferation of connected devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare, the attack surface has expanded significantly. From medical devices to wearable technologies, each endpoint represents a potential entry point for cybercriminals, necessitating a comprehensive and proactive cybersecurity approach.
Regulatory Compliance Challenges
Stringent data protection regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, add an additional layer of complexity. Ensuring compliance with these regulations is not only a legal requirement but also crucial for maintaining trust in the healthcare system.
The Critical Role of Staying Ahead in the Race Against Cyber Threats
As of 2023, a staggering 80% of healthcare organizations have experienced at least one data breach, emphasizing the urgent need for proactive cybersecurity strategies.
Proactive measures involve a combination of advanced technologies, employee training, and a comprehensive risk management approach. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are becoming indispensable tools for detecting anomalies and potential threats in real-time. Investing in these technologies is not just a security measure but a long-term cost-saving strategy, as the average cost of a healthcare data breach in 2022 was estimated to be $ 4.45 million.
The Aftermath of a Data Breach
Handling the aftermath of a data breach demands a strategic, comprehensive approach that encompasses financial considerations, reputation management, regulatory compliance, and operational recovery. By understanding the anatomy of a breach and the multifaceted consequences that follow, organizations can better position themselves to mitigate the impact and emerge stronger in an increasingly hostile cyber landscape.
Immediate Consequences for Healthcare Organizations
The immediate fallout of a data breach in healthcare is felt across multiple dimensions, ranging from financial to operational. According to recent studies, the average cost of a healthcare data breach is estimated to be around $4.45 million, taking into account direct expenses, regulatory fines, and the indirect costs associated with reputational damage and loss of business.
Financial Implications
Direct Costs: Immediate financial repercussions include the costs associated with incident investigation, system remediation, and legal fees. On average, these can account for 40% of the total expenses incurred.
Regulatory Fines: Non-compliance with data protection regulations, such as HIPAA in the United States, can lead to hefty fines. In 2020, the HHS Office for Civil Rights imposed fines ranging from $25,000 to $5.1 million for various healthcare data breaches.
Operational Disruptions
Healthcare organizations often face operational disruptions as they strive to contain and remediate the breach. A recent study revealed that 60% of healthcare entities experienced downtime lasting more than eight hours in the aftermath of a breach.
Long-term Repercussions on Patient Trust and Organizational Reputation
The aftermath of a data breach extends far beyond immediate financial losses. Perhaps the most significant long-term impact is the erosion of patient trust and damage to organizational reputation.
Patient Trust Erosion
Healthcare breaches expose sensitive patient data, eroding trust in the organization’s ability to safeguard personal information. A survey found that 80% of patients are concerned about the security of their healthcare data.
Reputational Damage
A data breach tarnishes the brand image of healthcare organizations. Research indicates that 54% of patients would switch healthcare providers if their current provider experienced a data breach.
Steps Taken in the Wake of a Breach
Incident Response Strategies for Mitigating Damage
Responding swiftly and effectively to a data breach is important in mitigating its impact. Establishing an incident response plan tailored to the healthcare sector is crucial.
Rapid Identification and Isolation: On average, it takes 326 days to identify and contain a healthcare data breach. Implementing advanced threat detection systems can significantly reduce this timeframe, minimizing the potential damage.
Forensic Analysis and Investigation: Post-breach, conducting a thorough forensic analysis helps understand the nature and scope of the breach. According to the HHS, organizations that contained the breach within 30 days save an average of $1million compared to those who take longer.
Importance of Communication and Transparency Post-Breach
Effective communication and transparency are key elements in rebuilding trust and mitigating reputational damage post-breach.
-
Timely Notification: A swift and transparent notification process is critical. Studies show that 73% of patients expects organizations to promptly notify them of a data breach.
-
Educational Campaigns: Launching educational campaigns to inform patients about cybersecurity measures and the steps taken post-breach fosters a sense of security. 90% of patients are more likely to trust organizations that engage in such initiatives.
Costs Incurred by Hospitals and Organizations
Understanding the immediate financial implications and the long-term reputational and operational costs of cybersecurity breaches is imperative for healthcare organizations.
Immediate Financial Implications
-
Incident Response and Investigation: The immediate response to a cyber incident involves hiring cybersecurity experts and investigators to assess the extent of the breach. According to Cybersecurity Ventures, the average cost of a data breach investigation is approximately $500,000.
-
System Remediation and Restoration: Hospitals must invest in restoring compromised systems and implementing robust security measures to prevent future attacks. The direct costs of system remediation can range from $1 million to $5 million, depending on the severity of the breach.
Potential legal and regulatory fines
-
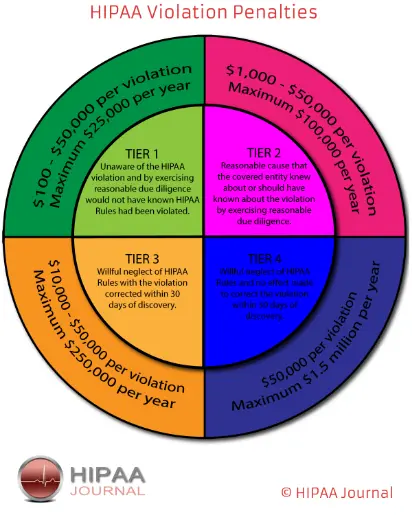
HIPAA Violations: Healthcare organizations face severe consequences for violating the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Fines for non-compliance can be staggering, with the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) imposing penalties ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million.
-
Other Regulatory Penalties: Beyond HIPAA, hospitals may face fines from other regulatory bodies, amplifying financial burdens. The Ponemon Institute reports that the average cost of regulatory fines for healthcare organizations is $2.5 million.
Long-Term Reputational and Operational Costs
-
Patient Trust Erosion: The aftermath of a cybersecurity breach can lead to a loss of trust among patients. According to a 2023 survey by HealthITSecurity, 54% of patients would consider changing their healthcare provider if their personal data was compromised in a cyberattack.
-
Long-Term Brand Damage: Rebuilding a tarnished reputation is a prolonged process. A study by Accenture revealed that 54% of healthcare consumers would likely switch providers if they perceived their current one as not adequately protecting their data.
Ongoing operational disruptions and recovery expenses
-
Downtime Costs: Cybersecurity incidents result in operational disruptions, leading to downtime. The average cost of downtime for a healthcare organization is estimated at $636,000 per hour.
-
Increased Cybersecurity Spending: Post-breach, hospitals must intensify their cybersecurity efforts. Cybersecurity Ventures predicts global spending on cybersecurity to surpass $1 trillion from 2021 to 2025, with healthcare accounting for a significant portion of this expenditure.
Evolving HIPAA Rules and Compliance
As the threat landscape in the digital realm continues to evolve, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) has undergone recent updates to ensure healthcare organizations remain resilient in the face of emerging cyber threats.
Recent Changes in HIPAA Regulations
The latest update, as of 2024, includes a heightened focus on digital health, interoperability, and the protection of electronic health information. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), the modifications aim to enhance patient access to their health information while reinforcing privacy and security measures. Key statistics indicate a surge in reported healthcare data breaches, with the number reaching 18 million records in the last year alone.
Implications for Healthcare Organizations in Terms of Data Protection
Recent statistics highlight the growing threat to healthcare data. From the year 2020-2021, the healthcare sector accounted for 85% of all data breaches. The updated HIPAA regulations aim to address vulnerabilities and enhance the protection of patient data. Non-compliance with these regulations can result in severe penalties, with fines ranging from $2500-$1.5 million per violation, emphasizing the critical importance of adapting security measures to stay compliant.
Managing Electronic Medical Records Security Challenges
By embracing proactive strategies such as advanced threat detection technologies and fostering collaborative efforts within the healthcare community, we can collectively strengthen our defenses against cyber threats.
The Unique Challenges Posed by Electronic Medical Records
Electronic Medical Records store a wealth of sensitive information, making them an attractive target for cybercriminals. According to a report by the Ponemon Institute, healthcare organizations experienced an average cost of $9.48 million per breach in 2021, emphasizing the severity of security lapses in the industry.
Additionally, the interconnected nature of healthcare systems and the diverse range of devices accessing EMRs create a complex attack surface. A staggering 79% of healthcare organizations faced a cybersecurity incident in the past two years, as reported by the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS).
The Need for Advanced Security Solutions
To combat the evolving threat landscape, healthcare providers must invest in advanced security solutions. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies play a pivotal role in threat detection and prevention. According to a study by Frost & Sullivan, the implementation of AI in healthcare cybersecurity is projected to reduce security.
Encryption is another crucial aspect of EMR security. In 2022, the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) reported that 87% of healthcare breaches could have been prevented through encryption, highlighting its significance in securing patient data.
Proactive Strategies for Enhanced Security
The Role of Advanced Threat Detection Technologies
Advanced threat detection technologies are indispensable in identifying and mitigating cyber threats in real-time. The use of behavioral analytics and anomaly detection can proactively identify unauthorized access or suspicious activities within EMR systems. A study by IBM Security found that organizations using advanced threat detection technologies had a lower cost of a data breach compared to those without such measures.
Collaborative Efforts within the Healthcare Community
Recognizing that healthcare cybersecurity is a shared responsibility, collaborative efforts within the healthcare community are crucial. Information sharing and joint initiatives can enhance the collective cybersecurity strength. The Health Information Sharing and Analysis Center (H-ISAC) reported a reduction in cyber threats among organizations actively participating in collaborative cybersecurity efforts.
The High Stakes of EMR Security
The reliance on Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) has become significant. The seamless integration of patient data and the accessibility of medical records have undoubtedly transformed the healthcare industry.
The True Cost of Inadequate Cybersecurity in Healthcare
The repercussions of inadequate cybersecurity in healthcare extend far beyond financial implications. IBM report reveals that the average cost of a data breach in the healthcare sector is $7.13 million, making it one of the most expensive industries to remediate cyber threats. Moreover, the healthcare sector consistently experiences the highest cost per stolen record, with an average of $429 per compromised record.
The impact of a data breach goes beyond monetary losses. Patients’ trust is eroded, and the reputational damage to healthcare providers can be long-lasting. A 2021 survey by Black Book Market Research found that 54% of patients would consider leaving their healthcare provider if they experienced a data breach.
The Value of Proactive Investment in Advanced Security Solutions
The growing sophistication of cyber threats necessitates a proactive approach to cybersecurity. Investing in advanced security solutions is not merely a preemptive measure; it is a strategic imperative. According to a report by Frost & Sullivan, the global healthcare cybersecurity market is projected to reach $10.85 billion by 2023, underscoring the escalating demand for cutting-edge security solutions.
Leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
The deployment of AI and ML in cybersecurity offers a dynamic defense against evolving threats. AI-driven solutions can analyze vast datasets in real-time, identifying anomalies and potential threats before they manifest. A study by Accenture indicates that AI can reduce security breaches by an estimated 43% and save the healthcare industry $150 billion annually by 2026.
Implementing Robust Encryption Practices
Encryption is a cornerstone of securing EMRs. A survey conducted by the American Medical Association (AMA) found that physicians believe that encrypting patient data is crucial for maintaining confidentiality. Implementing robust encryption practices not only safeguards patient information but also ensures compliance with regulatory standards such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Staying Informed and Ahead of the Curve
We’ll look into key strategies for staying informed and ahead of the curve, focusing on continuous monitoring of regulatory changes and the imperative need to invest in future-proof security solutions.
Continuous Monitoring of Regulatory Changes
Ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations, particularly the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), is important in our connected world. Continuous monitoring of evolving rules is not only a legal requirement but also a strategic move to maintain the trust of clients and partners.
HIPAA Evolution and Cybersecurity
According to the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), there have been notable updates to HIPAA rules, emphasizing the need for stringent cybersecurity measures to safeguard patient data.
Real-time Compliance Monitoring Tools
Implementing real-time compliance monitoring tools, allows organizations to stay ahead of regulatory changes.
Organizations that leverage such tools witness faster response times to regulatory updates, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
Investing in Future-Proof Security Solutions
By continuously monitoring and adapting to evolving compliance requirements and adopting cutting-edge technologies, we can not only ensure the security of EMRs but also maintains a competitive edge in an ever-changing cybersecurity landscape.
The Long-Term Benefits of Adopting Cutting-Edge Cybersecurity Technologies
The cybersecurity landscape is marked by rapid advancements, making it imperative for companies to invest in cutting-edge technologies to protect against emerging threats. According to a survey conducted by the Ponemon Institute, organizations that invest in advanced cybersecurity technologies experience a 50% reduction in the frequency and impact of cyber attacks.
Preparing for Future Compliance Requirements
Future-proofing security solutions goes beyond addressing current threats; it involves anticipating and preparing for future compliance requirements. As new laws and regulations are introduced, the ability to pivot quickly is a key differentiator. A case in point is the upcoming European Union Data Governance Act (DGA). Proactively investing in solutions that align with anticipated regulations allows organizations to maintain compliance without disruption.
The Role of Continuous Monitoring in Preventing Health Data Breaches
Continuous monitoring refers to the real-time surveillance and analysis of electronic systems, networks, and data to identify and respond promptly to potential security threats. In healthcare, where the stakes are exceptionally high due to the sensitivity of patient data, implementing continuous monitoring becomes a non-negotiable imperative.
Compliance Assurance
Stringent regulatory frameworks, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), mandate robust security measures to safeguard patient information. Continuous monitoring not only ensures compliance but also provides tangible evidence of a proactive commitment to data protection.
Early Detection of Insider Threats
A significant proportion of health data breaches stem from insider threats, whether intentional or inadvertent. Continuous monitoring helps identify unusual user behavior or internal anomalies, allowing organizations to address potential insider threats before they escalate.
Minimization of Downtime and Financial Loss
Health data breaches can cripple operations, resulting in downtime and substantial financial losses. Continuous monitoring minimizes the time between breach detection and response, limiting the impact on healthcare services and reducing the financial repercussions associated with data breaches.
Preservation of Patient Trust
Patient trust is the cornerstone of healthcare. Continuous monitoring reinforces a commitment to patient privacy and data security. By actively safeguarding electronic medical records, healthcare providers strengthen the bond of trust with their patients, which is indispensable in the digital age.
Technology and Software
Companies in the healthcare cybersecurity and EMR sector must establish and maintain a strong security overview. Our patent offers a strategic advantage by monitoring and surveillance of EMR application navigation to leverage the vast market potential as discussed in this report. By filtering out the fraudulent use by mapping the EMR application navigation, tech companies can showcase genuine customer satisfaction, enhancing their security and industry authority.
Read this original patent that is available for sale or licensing and addresses the top cybersecurity problems through surveillance and real time continuous monitoring technology.
Should you be interested in licensing or purchasing this patent portfolio to strengthen your position in this evolving technological landscape, or if you have any inquiries or require additional material, please contact us at hello@intellectualfrontiers.com.